
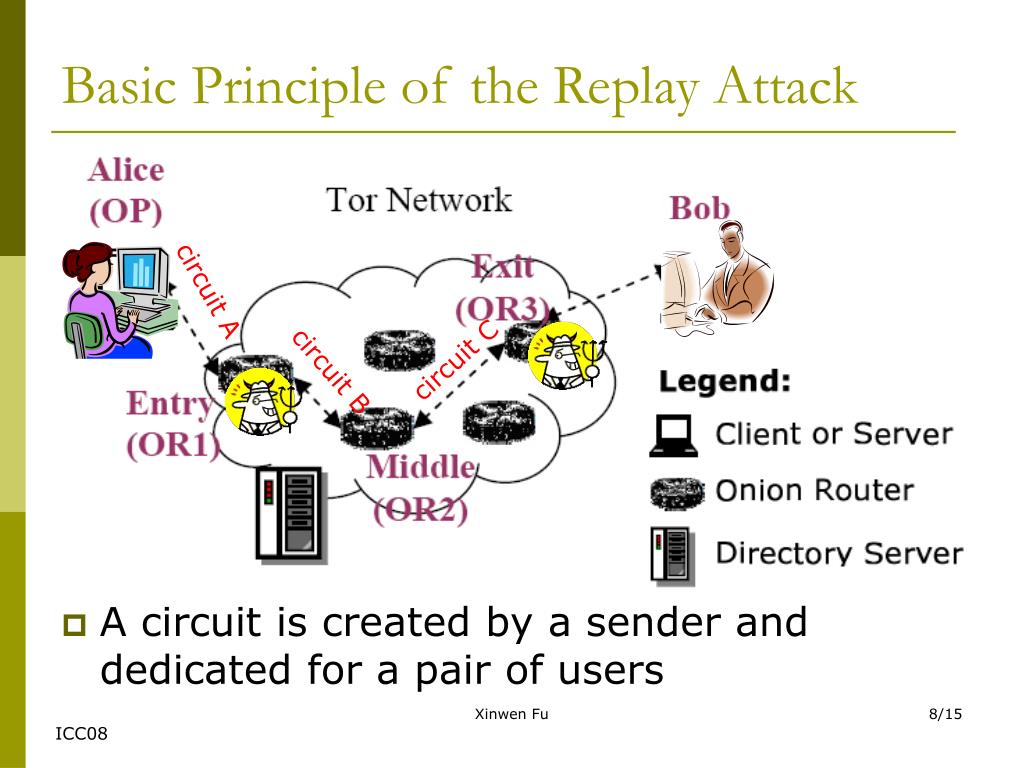
From human rights activists evading oppressive governments to drug dealers selling through online marketplaces, Tor is a popular way to gain significantly more anonymity than you would normally have online. At the 2005 IEEE Symposium, Steven Murdoch and George Danezis presented an article on security as it relates to traffic-analysis techniques. Tor (formerly an acronym for The Onion Router) is often touted as a way to browse the web anonymously. The Tor node, or exit relay, shows up as the actual communication originator rather than the sender.Įven though Tor prevents traffic analysis, it does not guard against traffic confirmation, or end-to-end correlation and tests. Within the Tor network, Internet traffic is sent to various routers, one at a time. Users who want their Internet searches to remain private use anonymity networking. This technology encrypts and then rebounds communications onto a network of relays run by volunteers throughout the world. Lisa Dittmer looks into the positive aspects of. In order to use Tor, users must run onion routing. Through the anonymization network Tor the name of the browser that leads to the darknet files can be easily encrypted and uploaded anonymously. I2P identity-sensitive networks are at once distributed and dynamic in nature and they route traffic through other peers. Another anonymity network is Freenet, which enables users to anonymously publish "freesites" as well as share files and chat on forums.
#TOR NETWORK DEFINITION SOFTWARE#
Tor software conceals the user's location and/or usage.
#TOR NETWORK DEFINITION FREE#
One open-source anonymity software free to public use is known as Tor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
